The technical side of security cameras and other precise details can be very difficult to understand, but very often, when you go through it would make more sense. Keeping up with the advancements or at least understanding its basics can be necessary. So, let’s get right into it and discuss the IPv4 address in brief detail.
What is IPv4?
Internet protocol is the set of rules that govern routing, transferring, and packetizing data when sent over a network. The Internet Protocol version 4 (IPv4) is the fourth version of the internet protocol. It is a necessary technology that allows your security cameras to connect to the web.
It is a predecessor of the recent IPv6 version. IPv4 is responsible for handling most of the internet traffic today. However, the main reason behind newer versions is that IPv4 is not available to all as it has reached its limits. As far as the numerical value is concerned, Internet Protocol version 4 addresses have 32-digit bits that can be shown in hexadecimal; an example would be:
00010001, 10001000,11111111, 00000001
This translates to 17.136.254.1, and each Ip address is unique.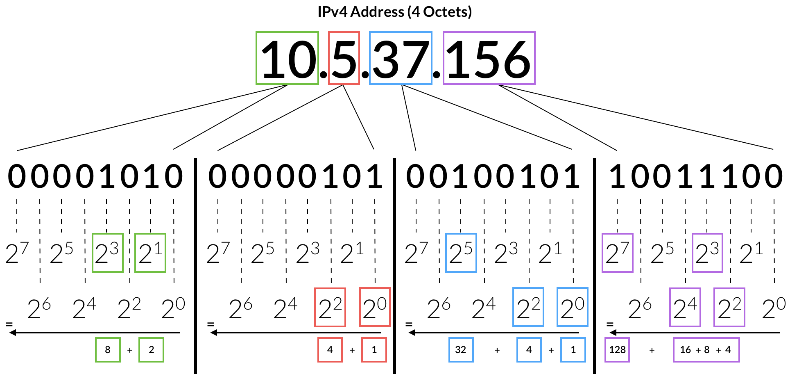
Benefits of internet protocol version 4
IPv4 offers a lot of benefits which is similar to the newer versions available today.
- Strong encryption: Without encryption, data cannot be sent securely and privately. IPv4 takes firm and established security measures to send data over a network in secured encryption. Data is encrypted in address packets.
- Connection of devices: IPv4 can connect to a wide range of security cameras and devices across a large network. Additionally, identity verification for each security camera or other device can be done easily without the use of Network Address Translation.
- Great flexibility: Addresses are combined very easily and quickly. In general, the routing process can be complex, but that is not the case in IPv4 as users can use multicast, and that further ensures enhanced communication.
- Data transmission: Seamless and safe data delivery can be expected with IPv4 because it delivers data packets right to the hosts and is used by transmission control protocol that is responsible for avoiding duplicate data transmission.


Comments
0 comments
Please sign in to leave a comment.